Search from website
Search from website
Icosagen has developed a specific 3D cell-based assay to identify human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA replication inhibitors in high-throughput format. In a proof of concept (PoC) study, 5 high-risk HPV specific inhibitors were identified that influence Tdp1 dependent DNA repair.
In this assay, a U2OS-based model system with dual-luciferase system was used to measure cell growth and toxicity of the compounds and HPV genome replication. U2OS cells which are derived from moderately differentiated osteosarcoma, have an adherent eptihelial morphology and carry wild-type p53 and pRB genes that have proven to be useful for studying various aspects of HPV life cycle.
Several types of human papillomaviruses (HPVs) may induce transformation of infected cells. Two main genera of HPVs are classified as mucosotropic α and cutaneous β HPVs, both including high-risk cancer-associated species. Regardless of being extensively studied for decades, treatment for HPV-related infections/diseases remain challenging. Three vaccines against clinically relevant HPV types have been developed with their efficacy approved. However, various social, economic and religious concerns limit their effect. Moreover, as the vaccines are not effective against established infection, it needs to administered at a very early age. Therefore no effective and specific cure against an ongoing HPV infection has not yet been developed.The absence of antiviral drugs has driven investigations into the details of the molecular mechanisms of the HPV life cycle, which is tightly linked to epithelial differentation. Viral helicase E1 and transcription factor E2 are phosporoteins, which play a pivotal role in the viral life cycle. For effective HPV genome replication, two viral proteins E1 and E2 form a complex. This protein-protein interaction has been an attractive target for developing anti-HPV drugs.
In addition to targeting HPV proteins, the viral genome itself could be target as well. Several sequence-specific DNA binding compounds have been developed, that bind to AT-rich regions near the E1 and E2 binding sites in the HPV replication origin and effictively reduce the stably maintained episomal viral genomes.
There are number of systems for conducting high-throughput screening (HTS) of available chemical libraries that is a widely used technique to identify new inhibitors of various diseases. Most of the work has been done in human primary epithelial keratinocytes. However, using these cells is relatively time consuming and expensive, especially for high-throughput screening.
1. Develop assay system for HT-screenIn Icosagen's U2OS cell-based assay, the dual-luciferase system is used to measure simultaneously:Cell growth (reflecting the cytotoxicity of the compounds)
HPV genome replication intensity
2. Generation of HPV marker genomes 3. Pilot study — screening of NCI Diversity Set IV Library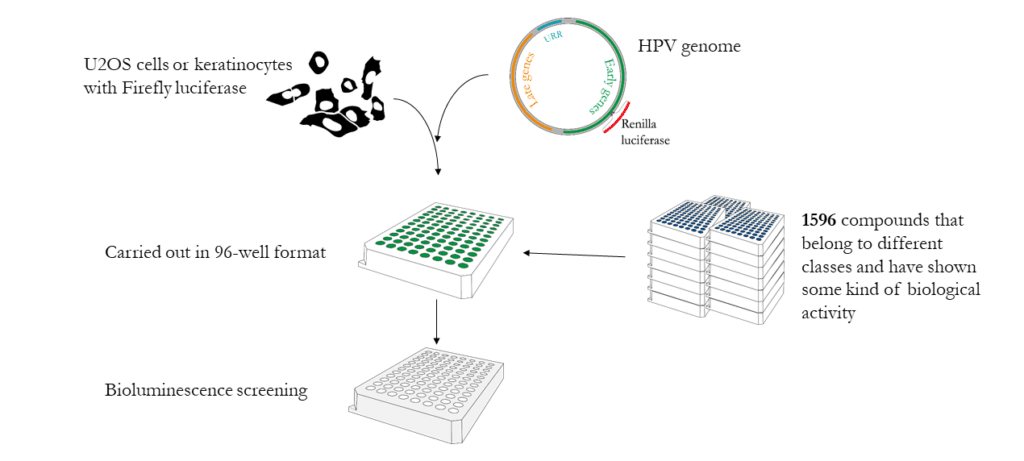
Icosagen model system was used to screen NCI Diversity Set IV library, which consists of different classes of biologically active compounds. 5 compounds were identified that inhibited HPV18 initial amplification in low-micro molar range. None of the identified compounds inhibit E1 and E2 dependent URR replication. Besides initial amplification four out of five compounds successfully inhibited stable maintenance phase of the viral replication. In addition three compounds inhibited vegetative amplification, which takes place in highly differentiated upper epithelia.
These inhibitors or their analogues are therefore capable of eliminating different stages of HPV infection. The identified compounds do not inhibit E1 and E2 dependent URR replication, indicating that different cellular proteins could be used to facilitate HPV genome replication and/or that the replication mechanism of viral genome differs from the URR plasmid replication.
For more information, please contact sales@icosagen.com 1 Toots M, et al. (2017) Identification of several high-risk HPV inhibitors and drug targets with a novel high-throughput screening assay. PLoS Pathog 13(2): e1006168.
Read the paper here



